| [1] Hosokawa Y, Hosokawa I, Ozaki K, et al. IL-27 Modulates Chemokine Production in TNF-α -Stimulated Human Oral Epithelial Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):1198-1206.[2] Hosokawa Y, Hosokawa I, Shindo S, et al. IL-4 Modulates CCL11 and CCL20 Productions from IL-1β-Stimulated Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1): 153-159.[3] Imai H, Fujita T, Kajiya M,et al. Mobilization of TLR4 Into Lipid Rafts by AggregatibacterActinomycetemcomitansin Gingival Epithelial Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(5):1777-1786.[4] Hans S, Mali AM. Estimation and comparison of osteopontin levels in plasma in subjects with healthy periodontium and generalized chronic periodontitis and its assessment after scaling and root planing. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2012;16(3): 354-357.[5] Rittling SR, Zetterberg C, Yagiz K, et al. Protective role of osteopontin in endodontic infection. Immunology. 2010;129(1): 105-114. [6] Salinas-Muñoz M, Garrido-Flores M, Baeza M, et al. Bone resorptive activity in symptomatic and asymptomatic apical lesions of endodontic origin. Clin Oral Investig. 2017;21(8): 2613-2618.[7] Persoon IF, Özok AR. Definitions and Epidemiology of Endodontic Infections. Current Oral Health Reports 2017; 4:278-285.[8] Azuma MM, Samuel RO, Gomes-Filho JE, et al. The role of IL-6 on apical periodontitis: a systematic review. Int Endod J. 2014;47(7):615-621.[9] Kalatzis-Sousa NG, Spin-Neto R, Wenzel A, et al. Use of micro-computed tomography for the assessment of periapical lesions in small rodents: a systematic review. Int Endod J. 2017;50(4):352-366..[10] Larsen T, Fiehn N. Dental biofilm infections - an update. APMIS. 2017;125(4):376-384.[11] Lu S, Zhang J, Zhou Z, et al. Synergistic inhibitory activity of zoledronic acid and paclitaxel on bone metastasis in nude mice. Oncol Rep. 2008;20(3):581-587.[12] Ang ES, Pavlos NJ, Chim SM, et al. Paclitaxel inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorption via influencing mitotic cell cycle arrest and RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and ERK. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(3):946-955.[13] Zheng X, Li Z, Chen L, et al. Self-Assembly of Porphyrin– Paclitaxel Conjugates Into Nanomedicines:Enhanced Cytotoxicity due to Endosomal Escape. Chem Asian J. 2016; 11(12):1780-1784[14] Kundranda M, Niu J. Albumin-bound paclitaxel in solid tumors: clinical development and future directions. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:3767-3777. [15] Drobecq H, Boll E, Sénéchal M,et al. A Central Cysteine Residue Is Essential for the Thermal Stability and Function of SUMO-1 Protein and SUMO-1 Peptide–Protein Conjugates. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27(6):1540-1546.[16] Huang Y, Liang W, Yang Y, et al. Phase I/II dose-finding study of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab®-Paclitaxel) plus Cisplatin as Treatment for Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:464. [17] Hurria A, Blanchard MS, Synold TW, et al. Age-Related Changes in Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Influence of Chronological Versus Functional Age. The Oncologist 2015; 20:37-44.[18] Kendra KL, Plummer R, Salgia R, et al. A Multicenter Phase I Study of Pazopanib in Combination with Paclitaxel in First-Line Treatment of Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14(2):461-469.[19] Oudin MJ, Barbier L, Schäfer C,et al. MENA Confers Resistance to Paclitaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16(1):143-155. [20] Rezazadeh M, Emami J, Hasanzadeh F, et al. In vivo pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and anti-tumor effect of paclitaxel-loaded targeted chitosan-based polymeric micelle. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(5):1707-1717.[21] Rugo HS, Barry WT, Moreno-Aspitia A,et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Paclitaxel Once Per Week Compared With Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Nab-Paclitaxel Once Per Week or Ixabepilone With Bevacizumab As First-Line Chemotherapy for Locally Recurrent or Metastatic Breast Cancer: CALGB 40502/NCCTG N063H (Alliance). J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(21):2361-2369.[22] Tamura K, Inoue K, Masuda N, et al. Randomized phase II study of nab-paclitaxel as first-line chemotherapy in patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(5):987-994.[23] Villaruz LC, Socinski MA. Is there a role of nab-paclitaxel in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer? The data suggest yes. Eur J Cancer. 2016;56:162-171. [24] Yang M, Yu T, Wang Y, et al. Vaginal Delivery of Paclitaxel via Nanoparticles with Non-Mucoadhesive Surfaces Suppresses Cervical Tumor Growth. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014;3(7): 1044-1052.[25] Sanchez-Torres A, Sanchez-Garces M, Gay-Escoda C. Materials and prognostic factors of bone regeneration in periapical surgery: A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2014;19(4):e419-25.[26] Qu C, Meng H, Han J. Implant periapical lesion - a review and a case report with histological evaluation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(9):1099-1104.[27] Petersson A, Axelsson S, Davidson T,et al. Radiological diagnosis of periapical bone tissue lesions in endodontics: a systematic review. Int Endod J. 2012;45(9):783-801.[28] Zoellner H. Dental Infection and Vascular Disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011;37(3):181-192.[29] Maeda H, Wada N, Nakamuta H, et al. Human periapical granulation tissue contains osteogenic cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;315(2):203-208.[30] Yilmaz E, Watkins SC, Gold MS. Paclitaxel-induced increase in mitochondrial volume mediates dysregulation of intracellular Ca2+ in putative nociceptive glabrous skin neurons from the rat. Cell Calcium. 2017;62:16-28.[31] Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Shi L, et al. Clinical Research on Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel-Based Chemotherapy for Advanced Esophageal Cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(12):4993-4996.[32] Zhang H, Li Y, de Carvalho-Barbosa M, et al. Dorsal Root Ganglion Infiltration by Macrophages Contributes to Paclitaxel Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J Pain. 2016; 17(7):775-786. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
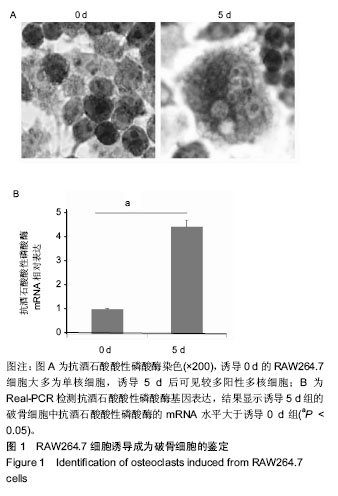
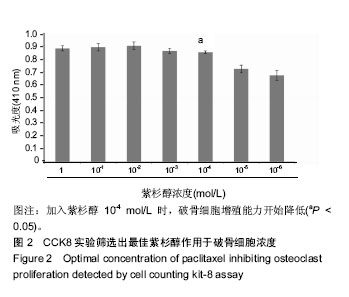
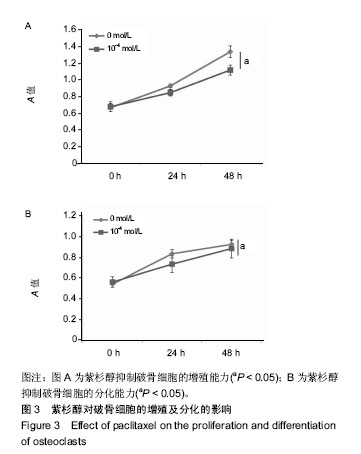
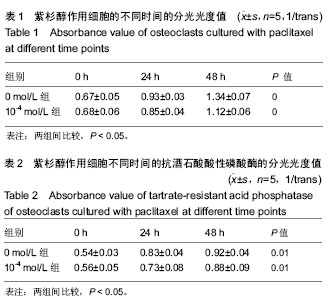
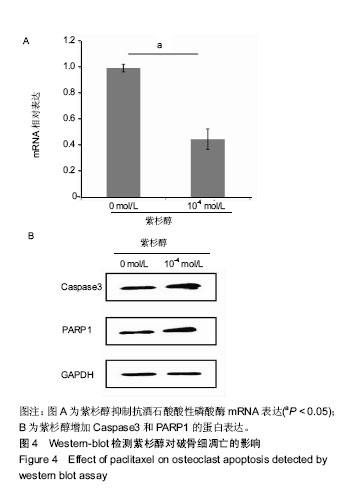
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
紫杉醇:主要是由红豆杉科植物中提取的一类产物。大量的研究表明紫杉醇广泛应用于恶性肿瘤的治疗。但是国内外对于紫杉醇治疗根尖周炎骨破坏的研究较少。#br#
破骨细胞:为多核细胞,由于破骨细胞本身生存周期较短,目前对于破骨细胞的培养主要采用破骨前体细胞,在体外对其进行诱导后形成成熟的破骨细胞。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
紫杉醇:主要是由红豆杉科植物中提取的一类产物。大量的研究表明紫杉醇广泛应用于恶性肿瘤的治疗。但是国内外对于紫杉醇治疗根尖周炎骨破坏的研究较少。#br#
破骨细胞:为多核细胞,由于破骨细胞本身生存周期较短,目前对于破骨细胞的培养主要采用破骨前体细胞,在体外对其进行诱导后形成成熟的破骨细胞。#br#
#br#